WHAT ARE MICROCONTROLLERS?
1. A microcontroller is a functional computer system on a chip. It contains a processor core, memory and programmable input/output peripherals.
2. Micro suggests that the device is small and controller tells you that the device might be used to controls objects, processes or events.
3. Another term to describe a microcontroller is embedded controller because the microcontroller and its support circuits are often build into or embedded in the devices they control.
- The CPU core - ranging from simple 4-bit processors to sophisticated 32/64-bit processors
- Memory (both ROM and RAM)
- Some parallel digital I/O
WHERE DO YOU FIND THEM?
Microcontrollers are hidden in tons of appliances, gadgets, and other electronics.
Basic Block Diagram of A Microcontroller
CPU
1. CPU does all the arithmetic and logic operations.
2. It controls the flow execution of instruction.
INPUT/OUTPUT PORTS (I/O
PORTS)
·
In order to make the microcontroller useful, it is necessary to
connect it to peripheral devices. Each microcontroller has one or more
registers (called a port) connected to the microcontroller pins.
ALU
1. An Arithmetic And Logic Unit (ALU) is a digital circuit that performs integer arithmetic and logical operations.
2. The ALU is a fundamental building block of the central processing unit of a computer, and even the simplest microprocessors contain one for purposes such as maintaining timers.
3. The processors found inside modern CPUs and graphics processing units (GPUs) accommodate very powerful and very complex ALUs; a single component may contain a number of ALUs.
RAM (RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY)
1. RAM hold the set of instructions (program), i.e. being executed by the CPU.
2. It holds important data required by the program.
3. It holds some important data structures like “stack”.
4. It is volatile in nature.
Main components of a microcontroller
INPUT/OUTPUT PORTS (I/O PORTS)
Most microcontrollers will also combine other devices such as:
- A Timer module to allow the microcontroller to perform tasks for certain time periods.
- A serial I/O port to allow data to flow between the microcontroller and other devices such as a PC or another microcontroller.
- An ADC to allow the microcontroller to accept analogue input data for processing.
A single chip microcontroller
The above figure illustrates a typical microcontroller device and the different sub units integrated onto the microcontroller microchip.
Microcontrollers are nowadays brimming with added functionality on this single IC and often include:
- Communications Peripherals: SPI, I2C™, UART, CAN, USB, Ethernet, IrDA®, LIN.
- Control Peripherals: capture/compare, counters, real-time clock & calendar, motor control & PWM
- Integrated Display Drivers: LED, LCD.
- On-chip internal oscillators and Phase-Locked Loop (closed loop feedback control).
- Analog Peripherals: A/D Converters, comparators, op amps, brown-out detection & reset, low voltage detection, temperature sensors, D/A Converters and voltage regulators.
REGISTER UNIT
1. Penumpok (accumulator)
· Menyimpan data yang di ambil dari ingatan sebelum dan selepas diproses oleh ALU.
2. Daftar suruhan (Instruction Register)
· Menyimpan arahan dan suruhan yang di ambil dari ingatan sebelum dinyahkod oleh penyahkod suruhan.
3. Pembilang Aturcara (Program counter)
· Menyimpan alamat bagi suruhan berikutnya yang akan dilaksanakan pleh mikropemproses.
· Alamat yang di pegang oleh PC akan dinaikkan setiap kali suruhan di ambil dari ingatan bagi memastikan suruhan berikutnya di ambil pada kitar yang menyusul
· Jumlah kenaikan PC adalah mengikut byte Kod Mesin bagi suatu suruhan yang dilaksanakan.
4. Daftar Status (status register)
· Menyimpan maklumat mengenai hasil operasi ALU yang terakhir dalam bentuk bit-bit.
· Bit-bit ini dikenali sebagai bendera (flag).
· Flag boleh bernilai 1 (SET) atau 0 (RESET).
INPUT/OUTPUT PORTS (I/O PORTS)
In order to make the microcontroller useful, it is necessary to connect it to peripheral devices. Each microcontroller has one or more registers (called a port) connected to the microcontroller pins.
Why do we call them input/output ports? Because it is possible to change a pin function according to the user's needs. These registers are the only registers in the microcontroller the state of which can be checked by voltmeter!
HOW DOES THE MICROCONTROLLER OPERATE?
8051 MICROCONTROLLER APPLICATIONS:
Advantages
of Microcontrollers
Disadvantages of Microcontrollers
Applications
HOW DOES THE MICROCONTROLLER OPERATE?
Even though there is a large number of different types of microcontrollers and even more programs created for their use only, all of them have many things in common. Thus, if you learn to handle one of them you will be able to handle them all. A typical scenario on the basis of which it all functions is as follows:
1. Power supply is turned off and everything is still…the program is loaded into the microcontroller, nothing indicates what is about to come…
2. Power supply is turned on and everything starts to happen at high speed! The control logic unit keeps everything under control. It disables all other circuits except quartz crystal to operate. While the preparations are in progress, the first milliseconds go by.
3. Power supply voltage reaches its maximum and oscillator frequency becomes stable. SFRs are being filled with bits reflecting the state of all circuits within the microcontroller. All pins are configured as inputs. The overall electronis starts operation in rhythm with pulse sequence. From now on the time is measured in micro and nanoseconds.
4. Program Counter is set to zero. Instruction from that address is sent to instruction decoder which recognizes it, after which it is executed with immediate effect.
MICROPROCESSOR
VS MICROCONTROLLER
Microprocessor
|
Microcontroller
|
CPU is stand –
alone , RAM , ROM, IO, timer are separate
|
CPU, RAM, ROM, IO
and timer are all on a single chip
|
Designer can
decide on the amount of ROM, RAM and I/O ports
|
Fix amount of
on-chip ROM, RAM and I/O ports
|
expensive
|
For applications
in which cost, power and space are critical
|
General-purpose
|
Single-purpose
|
EVOLUTION
MICROCONTROLLER
1)
The Intel bagged the credit of producing the first
microcontroller 8048 with a CPU and 1K bytes of EPROM , 64 bytes of RAM an
8-bit timer and 27 I/O pin in 1976.
2)
Then followed the most popular controller 8051 in
the year 1980 with 4K bytes of ROM, 128 bytes of RAM, a serial port, two 16-bit
timer, and 32 I/O pins.
3)
The 8051 family has many additions and improvements
over the years and remains a most soughtafter tool for today circuit designers.
4)
The same intel introduced a 16 bit controller 8096 in the year 1982
5)
Later intel introduced 80c196 series of 16-bit microcontroller
for mainly industrial applications
6)
Microchip, another company has introduced a
microcontroller PIC 16C64 an 8-bit in the year 1985
7)
32-bit microcontrollers has developed by IBM and
Motorola-MPC 505 is a 32-bit RISC controller of Motorola .
8)
The 404 GA is a 32-bit RISC embedded controller of
IBM
TYPES
OF MICROCONTROLLER
Cpu
(Central Processor Unit)
As
you may be familiar that Central Processor Unit or CPU is the mind of any
processing machine. It scrutinizes and manages all processes that are carried out
in the Microcontroller. User has no power over the functioning of CPU. It
interprets program printed in storage space (ROM) and carries out all of them
and do the projected duty.
Interrupts
As
the heading put forward, Interrupt is a sub-routine call that reads the
Microcontroller’s key function or job and helps it to perform some other
program which is extra important at that point of time. The characteristic of
Interrupt is extremely constructive as it aids in emergency cases. Interrupts
provides us a method to postpone or delay the current process, carry out a
sub-routine task and then all over again restart standard program
implementation.
The
Micro-controller 8051 can be assembled in such a manner that it momentarily
stops or break the core program at the happening of interrupt. When sub-routine
task is finished then the implementation of core program initiates
automatically as usual. There are 5 interrupt supplies in 8051 Microcontroller,
two out of five are peripheral interrupts, two are timer interrupts and one is
serial port interrupt.
Memory
Micro-controller
needs a program which is a set of commands. This program enlightens
Microcontroller to perform precise tasks. These programs need a storage space
on which they can be accumulated and interpret by Microcontroller to act upon
any specific process. The memory which is brought into play to accumulate the
program of Microcontroller is recognized as Program memory or code memory. In
common language it’s also known as Read Only Memory or ROM.
Micro-controller
also needs a memory to amass data or operands for the short term. The storage
space which is employed to momentarily data storage for functioning is
acknowledged as Data Memory and we employ Random Access Memory or RAM for this
principle reason. Microcontroller 8051 contains code memory or program memory
4K so that is has 4KB Rom and it also comprise of data memory (RAM) of 128
bytes.
Bus
Fundamentally
Bus is a group of wires which functions as a communication canal or mean for
the transfer Data. These buses comprise of 8, 16 or more cables. As a result, a
bus can bear 8 bits, 16 bits all together. There are two types of buses:
1. Address
Bus: Microcontroller
8051 consists of 16 bit address bus. It is brought into play to address memory
positions. It is also utilized to transmit the address from Central Processing
Unit to Memory.
2. Data
Bus: Microcontroller
8051 comprise of 8 bits data bus. It is employed to cart data.
Oscillator
As
we all make out that Microcontroller is a digital circuit piece of equipment,
thus it needs timer for its function. For this function, Microcontroller 8051
consists of an on-chip oscillator which toils as a time source for CPU (Central
Processing Unit). As the productivity thumps of oscillator are steady as a
result, it facilitates harmonized employment of all pieces of 8051
Microcontroller. Input/output Port: As we are acquainted with that
Microcontroller is employed in embedded systems to manage the functions of
devices. Thus to gather it to other machinery, gadgets or peripherals we need
I/O (input/output) interfacing ports in Micro-controller. For this function
Micro-controller 8051 consists of 4 input/output ports to unite it to other
peripherals.
Timers/Counters: Micro-controller 8051 is incorporated with two 16 bit counters & timers. The counters are separated into 8 bit registers. The timers are utilized for measuring the intervals, to find out pulse width etc.
Timers/Counters: Micro-controller 8051 is incorporated with two 16 bit counters & timers. The counters are separated into 8 bit registers. The timers are utilized for measuring the intervals, to find out pulse width etc.
IMPORTANT
FEATURES OF 8051
1)
4K bytes ROM
2)
128K bytes RAM
3)
Four 8-bit I/O port
4)
Two 16-bit timer
5)
Serial interface
6)
64K external code memory space
7)
64K data memory space
PIN
DESCRIPTION OF THE 8051
Ø
The 8051 is a 40 pin device, but out of these 40
pins, 32 are used for I/O
Ø
24 of these are dual purpose, i.e they are operate
as I/O or control line or as part of the address or date bus
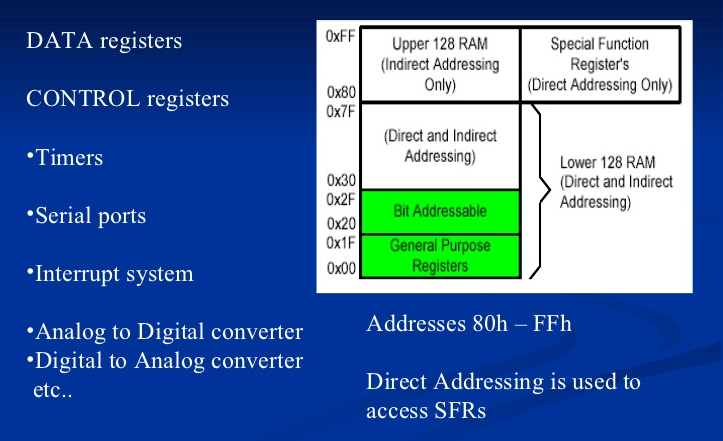
SPECIAL
FUNCTION REGISTER
LIST
OF REGISTER
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF 8051
8051 MICROCONTROLLER APPLICATIONS:
The
microcontroller 8051 has been in application in a large amount of machines,
principally because it is simple to incorporate in a project or to assemble a
machine around it. The following are the key spots of spotlight:
1. Energy Management: Competent
measuring device systems aid in calculating energy consumption in domestic and
industrialized applications. These meter systems are prepared competent by
integrating microcontrollers.
2. Touch screens: A
high degree of microcontroller suppliers integrate touch sensing abilities in
their designs. Transportable devices such as media players, gaming devices
& cell phones are some illustrations of micro-controller integrated with
touch sensing screens.
3. Automobiles: The
microcontroller 8051 discovers broad recognition in supplying automobile
solutions. They are extensively utilized in hybrid motor vehicles to control
engine variations. In addition, works such as cruise power and anti-brake
mechanism has created it more capable with the amalgamation of
micro-controllers.
4. Medical Devices: Handy
medicinal gadgets such as glucose & blood pressure monitors bring into play
micro-controllers, to put on view the measurements, as a result, offering
higher dependability in giving correct medical results.
Advantages
of Microcontrollers
The main
advantages of microcontrollers are given.
a)
Microcontrollers act as a microcomputer without any digital parts.
b)
As the higher integration inside microcontroller reduce cost and size of the
system.
c)
Usage of microcontroller is simple, easy for troubleshoot and system
maintaining.
d)
Most of the pins are programmable by the user for performing different
functions.
e)
Easily interface additional RAM, ROM,I/O ports.
f)
Low time required for performing operations.
Disadvantages of Microcontrollers
a)
Microcontrollers have got more complex architecture than that of
microprocessors.
b)
Only perform limited number of executions simultaneously.
c)
Mostly used in micro-equipments.
d)
Cannot interface high power devices directly.
Applications
Microcontrollers
are widely used in modern electronics equipments. Some basic applications of
microcontroller is given below.
a)
Used in biomedical instruments.
b)
Widely used in communication systems.
c)
Used as peripheral controller in PC.
d)
Used in robotics.
e)
Used in automobile fields.















No comments:
Post a Comment